The Benefits and Drawbacks of Cloud Computing
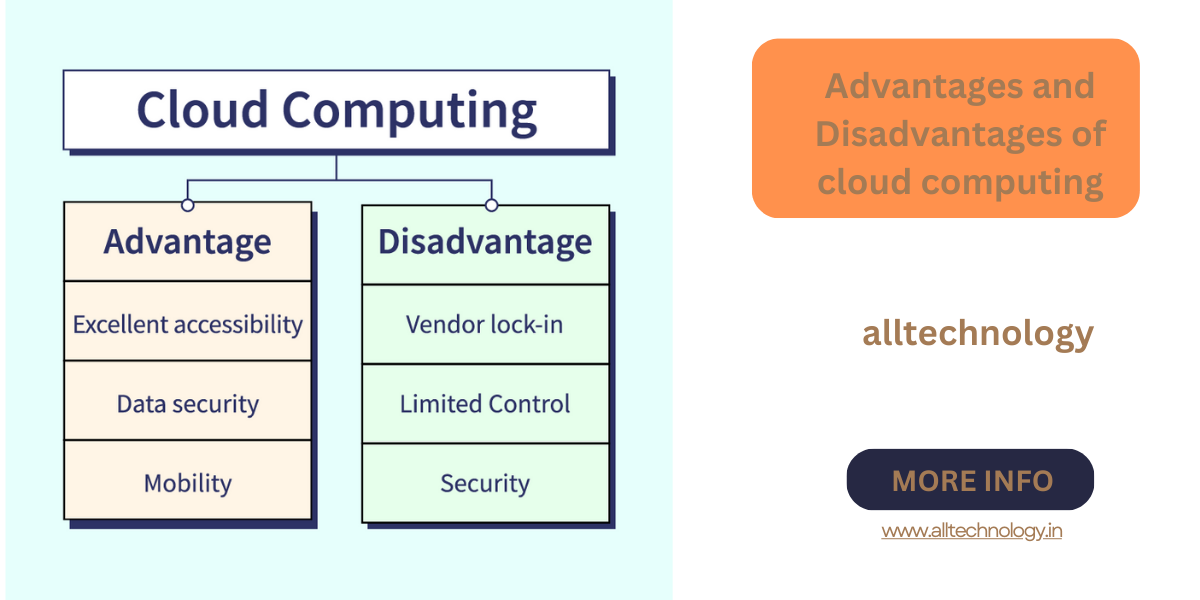
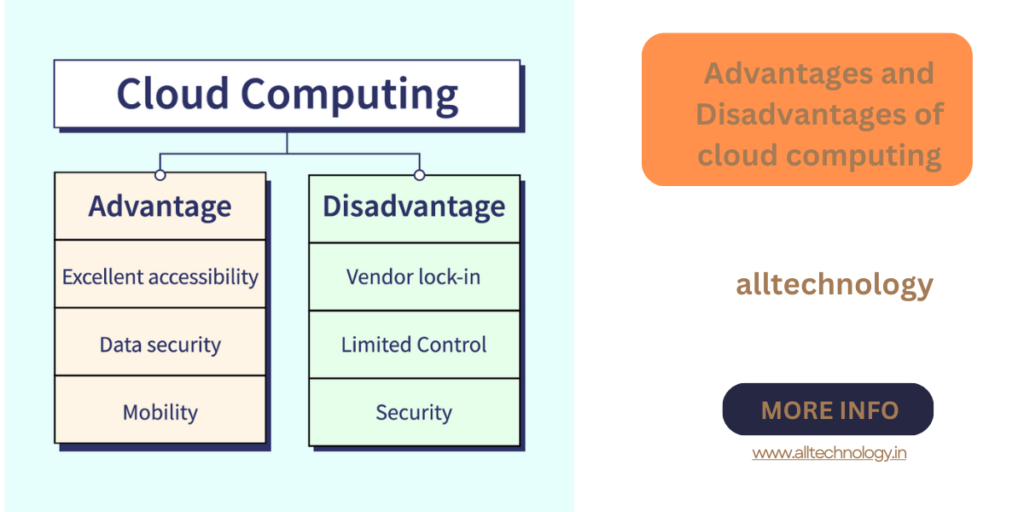
Advantages
- Data Backup and Restoration: Cloud computing facilitates seamless data backup and recovery, ensuring business continuity.
- Improved Collaboration: Teams can collaborate effortlessly through shared cloud storage, boosting productivity.
- Excellent Accessibility: Data is accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, supporting remote work.
- Cost-effective Maintenance: Reduced hardware and software maintenance costs as cloud providers handle updates.
- Upkeep and Updates: Providers manage infrastructure updates, freeing IT teams for strategic tasks.
- Mobility: Access cloud data via mobile devices, enhancing flexibility and productivity.
- Pay-per-use Model: Economical as businesses pay only for utilized services, offering budget flexibility.
- Scalable Storage Capacity: Virtually limitless data storage, catering to diverse data types.
- Enhanced Data Security: Advanced security measures by providers ensure data safety.
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Reliable disaster recovery options through data redundancy and backup systems.
- Agility and Innovation: Rapid adoption of new technologies, fostering innovation.
- Green Computing: Efficient resource use reduces energy consumption and e-waste.
Cloud computing is revolutionizing business operations with its myriad benefits. It provides a swift, efficient method for data backup and restoration, enhancing data accessibility and mobility. Teams can collaborate seamlessly through shared storage, boosting productivity. Organizations save on hardware and software maintenance costs, as cloud providers handle updates and security. The pay-per-use model offers financial flexibility, and scalable storage meets diverse data needs. Cloud computing also enhances security with advanced encryption and facilitates disaster recovery, ensuring business continuity.
Cost Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of cloud computing is its cost efficiency. Traditional IT infrastructure requires substantial capital investment for hardware, software, and maintenance. In contrast, cloud services operate on a pay-as-you-go model, significantly reducing upfront costs. Businesses can scale resources up or down based on demand, ensuring they only pay for what they use. This scalability not only cuts costs but also offers unparalleled flexibility, allowing businesses to adapt quickly to changing market conditions.
Accessibility and Collaboration
Cloud computing enhances accessibility and collaboration. Data stored in the cloud can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, breaking down geographical barriers and enabling remote work. Teams can collaborate in real-time, sharing and editing documents seamlessly. This level of accessibility fosters innovation and productivity, as employees can work efficiently from any location.
Disaster Recovery and Backup
Another critical benefit is the improved disaster recovery and backup solutions. Cloud providers offer robust backup and recovery options, ensuring data integrity and availability even in the face of catastrophic events. Businesses no longer need to worry about data loss due to hardware failures, natural disasters, or cyber-attacks, as cloud services often include automated backups and redundancy.
Disadvantages
- Vendor Reliability and Downtime: Potential for service interruptions due to technical issues or cyberattacks, affecting business operations.
- Internet Dependency: Dependence on a stable internet connection, risking delays during connectivity issues.
- Limited Control and Customization: Standardized services may not fully meet unique organizational needs.
- Data Security and Privacy Concerns: Trust in providers’ security protocols is crucial, as data breaches can have severe repercussions.
- Hidden Costs and Pricing Models: Additional fees for data transfer, storage, and specialized support can inflate costs.
- Dependency on Service Provider: Reliance on providers’ stability and policies can pose risks if they face financial troubles.
- Data Location and Compliance: Compliance challenges due to data stored across multiple jurisdictions with varying laws.
However, cloud computing has its challenges. Service outages or downtime can disrupt operations. Reliable, high-speed internet is crucial, and connectivity issues can hinder access. Limited control over customization may pose problems for businesses with specific needs. Security and privacy concerns arise with sensitive data stored on the cloud, demanding trust in providers’ measures. Hidden costs and pricing complexities can also be problematic. Dependency on a single provider for reliability and compliance with various data laws across regions adds to the complexity.
Security and Privacy Concerns
Despite its many benefits, cloud computing also poses significant security and privacy concerns. Storing sensitive data on third-party servers can be risky, as it may be vulnerable to breaches and unauthorized access. Businesses must ensure that their cloud providers have stringent security measures and compliance with industry standards. The shared nature of cloud environments can sometimes lead to data leakage or accidental exposure, making robust security practices essential.
Downtime and Reliability
Downtime and reliability are also potential disadvantages. Cloud services depend on internet connectivity, and any disruption in service can lead to significant downtime. This can affect business operations, especially for companies that rely heavily on cloud-based applications. While reputable cloud providers strive for high uptime, outages can still occur, underscoring the need for contingency plans.
Limited Control and Flexibility
Additionally, using cloud services can result in limited control and flexibility. Businesses may find themselves dependent on their cloud provider’s infrastructure and policies. Customization options might be restricted, and migrating data or services between different cloud providers can be challenging. This dependency can sometimes hinder a company’s ability to tailor solutions to their specific needs.
Conclusion
Cloud computing offers a myriad of advantages, from cost savings and enhanced collaboration to improved disaster recovery. However, it is not without its challenges, such as security risks, potential downtime, and limited control. By carefully weighing these pros and cons, businesses can make strategic decisions that align with their goals and ensure they harness the full potential of cloud technology.
FAQ
Question 1. What are the advantages and disadvantages with cloud computing?
- Advantage #1: Disaster Recovery (DR).
- Advantage #2: Access your data anywhere.
- Advantage #3: Low cost
- Advantage #4: Scalability.
- Advantage #5: Security.
- Disadvantage #1: Lack of total control.
- Disadvantage #2: Difficult to migrate.
- Disadvantage #3: Requires Internet.
Question 2. What are 5 advantages of cloud storage?
- Accessibility and redundancy.
- Data security.
- Ability to collaborate on documents and files.
- Scalability.
- Cost and resource savings.
- Compliance with legislation and regulations for storing data.
- Archives and backup data.